In our ever-growing quest for sustainable solutions to manage waste and reduce our carbon footprint, industrial composting has been hailed as a game-changer. The idea is as simple as it is appealing: transform organic waste into nutrient-rich soil that can be used to fertilize crops and gardens, closing the loop in a circular economy. However, despite its potential and the widespread enthusiasm, industrial composting faces significant challenges that sometimes render the process inefficient or even unworkable. This article seeks to delve deeper into these challenges and explore why industrial composting doesn’t always work as intended.
Understanding Industrial Composting
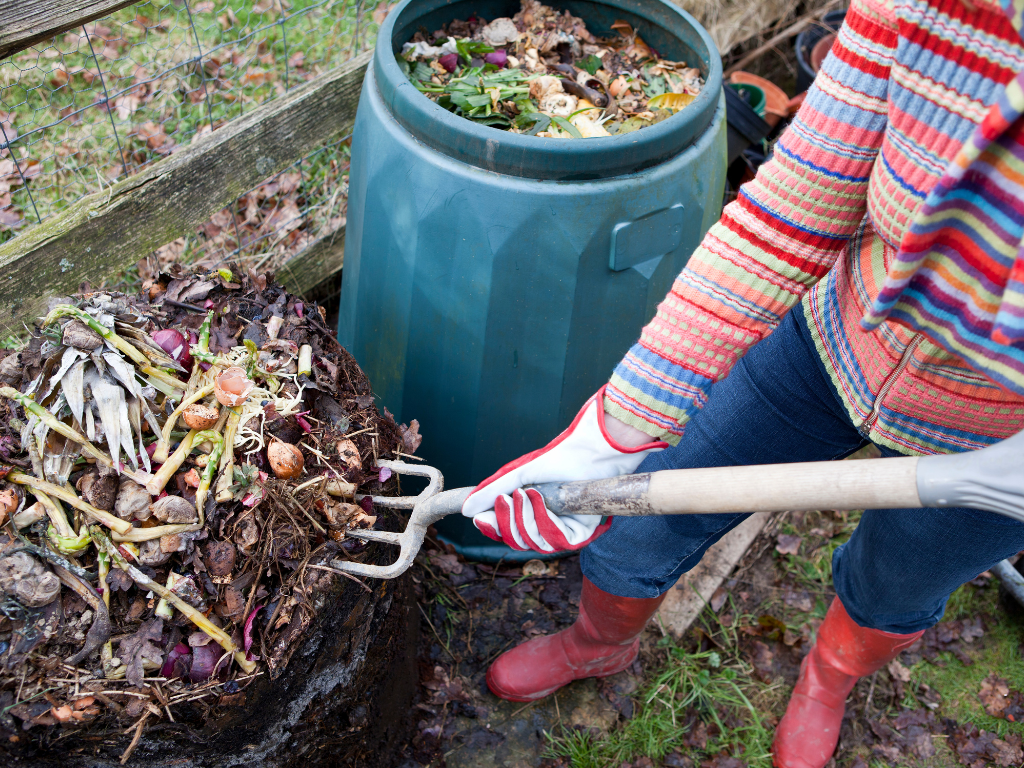
Before we dive into the issues, let’s first establish a clear understanding of what industrial composting is. Essentially, it’s a controlled process of organic waste breakdown on a large scale. Through the action of microorganisms, organic materials such as food scraps, yard waste, and certain types of biodegradable waste are transformed into compost, a soil-like material rich in nutrients. This process, when done correctly, can significantly reduce the volume of waste going to landfills and produce valuable products for agriculture and gardening.
Challenges
Despite its promise, industrial composting faces multiple challenges that are often complex and intertwined. Here are some of the most pressing:
1. Contamination
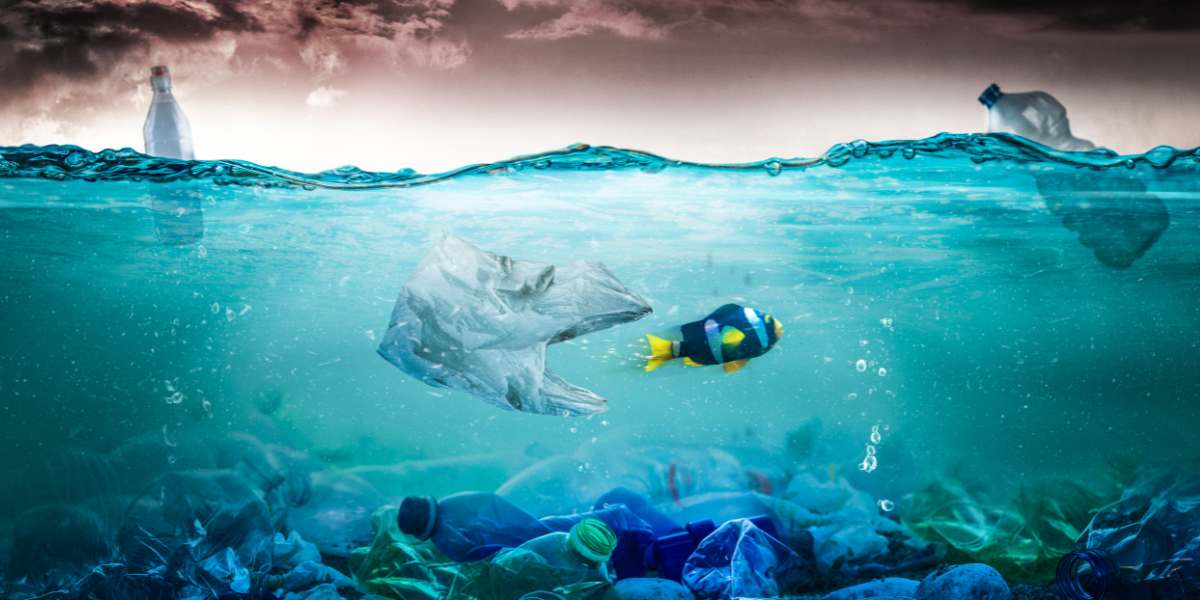
One of the most significant challenges in industrial composting is contamination. This primarily happens when non-compostable materials, such as plastics, glass, and metals, are mixed with compostable waste. These contaminants can be difficult to sort out and can degrade the quality of the resulting compost. Worse, if plastics break down into microplastics, they can end up in the soil and waterways, causing environmental harm.
2. Inconsistent Feedstock
The quality and characteristics of the organic waste used in composting, also known as the feedstock, can vary widely. This inconsistency can affect the composting process and the quality of the final product. For instance, a high amount of woody waste can slow down the composting process, while an overabundance of nitrogen-rich food waste can lead to odor issues.
3. Lack of Public Awareness and Participation
A successful industrial composting system requires active participation from the public. However, lack of awareness about what can and cannot be composted often leads to contamination. Furthermore, not all communities have access to industrial composting facilities, and many lack curbside collection programs for compostable waste, limiting the scope of these initiatives.
4. Regulatory Hurdles
The regulatory landscape for industrial composting varies from place to place and is often complex. Some regulations can inadvertently make it difficult to establish new composting facilities, while others may not adequately address issues such as odor control or environmental protections.
5. Economic Viability
Lastly, the economic viability of industrial composting is a significant challenge. The process requires substantial investments in infrastructure, equipment, and labor. Furthermore, the market for compost products is often uncertain, and composting facilities have to compete with synthetic fertilizers that are sometimes cheaper and more convenient to use.
Why Composting Doesn’t Always Work
Given these challenges, it’s clear that industrial composting doesn’t always deliver on its promises. Contamination can lead to low-quality compost or environmental harm, inconsistent feedstock can result in inefficient operations, and lack of public participation can limit the amount of waste that’s diverted from landfills. Regulatory hurdles can prevent the establishment of new facilities, while economic challenges can make it hard for existing ones to stay afloat.
Plastic Composting and the Role of Plastic IQ Technology
Plastic IQ technology has emerged as a potential game-changer in the realm of plastic waste management. Specifically, using bio-transformative plastics significantly shifts how we approach plastic waste. Bio-transformative plastics are designed to degrade in the presence of oxygen, light, and heat over a period of time, eventually breaking down into biodegradable components. This technology promises recyclability and compostability, which could revolutionize plastic waste management if widely adopted.
The ability to compost plastic waste is an attractive proposition. Currently, most plastic is in landfills or pollutes our oceans and landscapes because it does not break down naturally. Bio-transformative plastics, however, promise to change this narrative by transforming plastic waste into a material that can be composted industrially. This means that plastic waste could potentially be diverted from landfills and turned into a resource, contributing to the circular economy.
However, introducing these new types of plastics has been met with resistance from some stakeholders, particularly those invested heavily in traditional composting processes. The primary reason lies in the economic dynamics of the composting industry.
The composting industry, like many others, is driven by economics. Traditional compost, derived from organic waste like food scraps and yard waste, has a well-established market. It’s used extensively in agriculture and gardening, and composting facilities have a financial incentive to produce as much of it as possible. Introducing a new input—especially one as controversial and complex as plastic—poses significant risks and uncertainties.
Firstly, composting bio-transformative plastics requires precise control over conditions to ensure complete degradation, which can be more complex and costly than composting organic waste. Furthermore, there is uncertainty about whether compost that includes degraded plastic will be as marketable as traditional compost. If customers are wary of plastic-derived compost, it could hurt the bottom line of composting facilities.
Additionally, there’s an inherent conflict of interest. Composting facilities make money by processing organic waste, and they depend on a steady stream of this waste to stay profitable. Biodegradable or bio-transformative solutions like Plastic IQ threaten to disrupt this stream by reducing the amount of organic waste that needs composting. If plastic waste can be composted or biotransformed into other products, it could compete with traditional composting processes, impacting economic viability.
Thus, while Plastic IQ technology and similar innovations promise more sustainable plastic waste management, their adoption faces significant hurdles. Not only do they need to overcome technical and regulatory challenges, but they also have to navigate the complex economic dynamics of the waste management industry. Until these challenges are addressed, it’s likely that some stakeholders will remain resistant to these new solutions.