The year was 2022-23, and the globally renowned Ocean Race was well underway, carving its path through some of the world’s remotest seas. The sailors, equipped with the unyielding spirit of exploration, were discovering new challenges on their journey, but not the kinds they had been expecting.
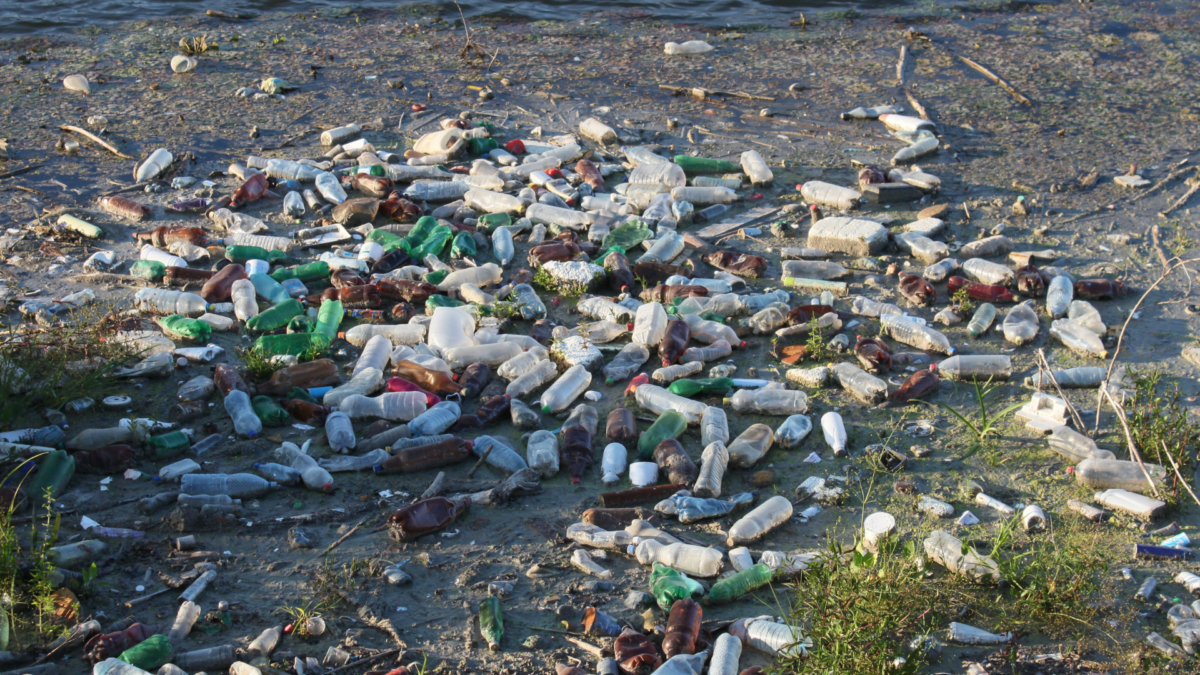
What should have been a thrilling global competition quickly became a stark revelation of the escalating pollution crisis. The yachtsmen found microplastic concentrations in these remote seas up to 18 times higher than during the last race held in 2017-18, reports The Guardian.
The Ocean Race, a prestigious event that has taken place every three to four years since 1973, offers a rare opportunity for scientists and sailors to examine remote parts of the ocean. They use this platform to investigate the conditions in these less-studied areas, measuring microplastic concentrations as they traverse the globe.
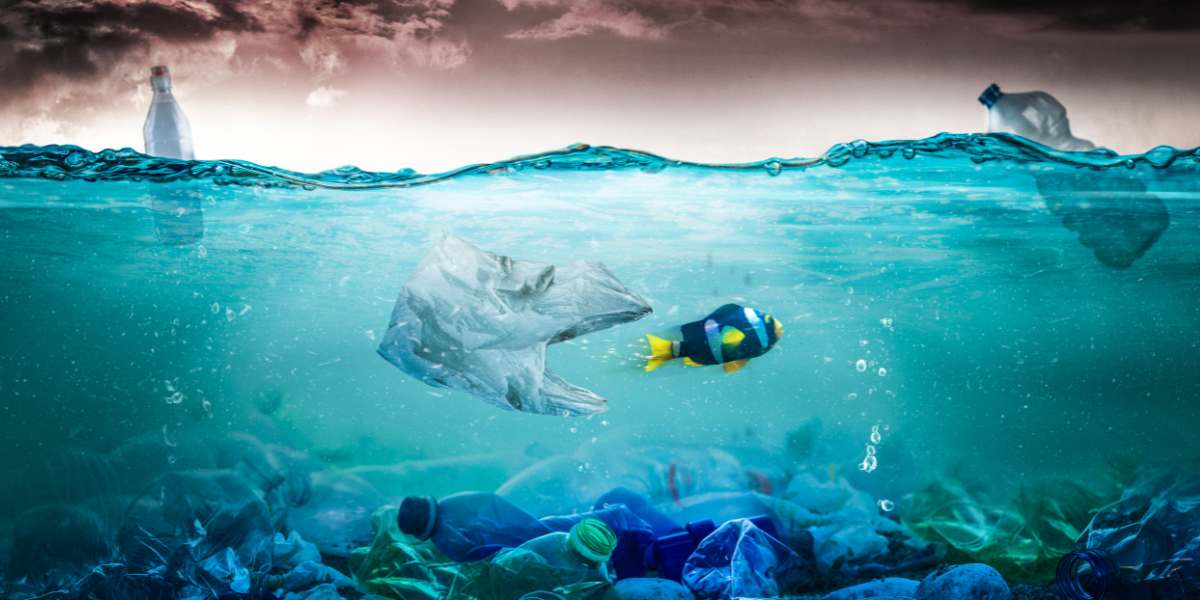
These microplastics, tiny fragments shed from larger plastic products, have insidiously spread throughout the world within just a century. They are now found everywhere – from the ocean’s deepest trenches to the air we breathe and even inside the human body. The health implications of this ubiquitous presence are still largely unknown, yet the sheer volume of these microplastics – estimated to be around 170 trillion particles, equating to about 21,000 per person on Earth – signals an alarming scenario.
During the 2022-23 Ocean Race, vessels used a filter to collect particles from the water, capturing anything measuring between 0.03 and 5 millimeters. These samples were then sent to the National Oceanography Centre (NOC) in the U.K for analysis. The results were disturbing: there were significantly higher levels of microplastics than ever before, with some areas recording up to 1,884 particles per cubic meter of seawater. Even the waters near Point Nemo, the furthest spot from land on the ocean’s surface, showed a concerning rise, with 320 particles per cubic meter, up from just nine to 41 during the previous race in 2017-18.
Why should we worry about these numbers? Victoria Fulfer, a scientist visiting the NOC from the University of Rhode Island, expressed her concerns stating, “It’s really concerning that we are finding microplastics in every sample, from coastal areas to the most remote regions of the ocean. We are seeing much higher concentrations this year, which can be a sign of increased pollution, but also is related to the increased sensitivity of our analysis.” These revelations expose the severity of our plastic pollution problem – a problem that is far worse than we imagined and continues to escalate.
In the face of this daunting challenge, scientists are working tirelessly to find ways to filter out or treat microplastics, while governments worldwide have started banning major offenders like polystyrene foam. However, the solution to this crisis goes beyond reactive measures; we must attack this issue at its root by transforming the very nature of the plastic we produce and use.
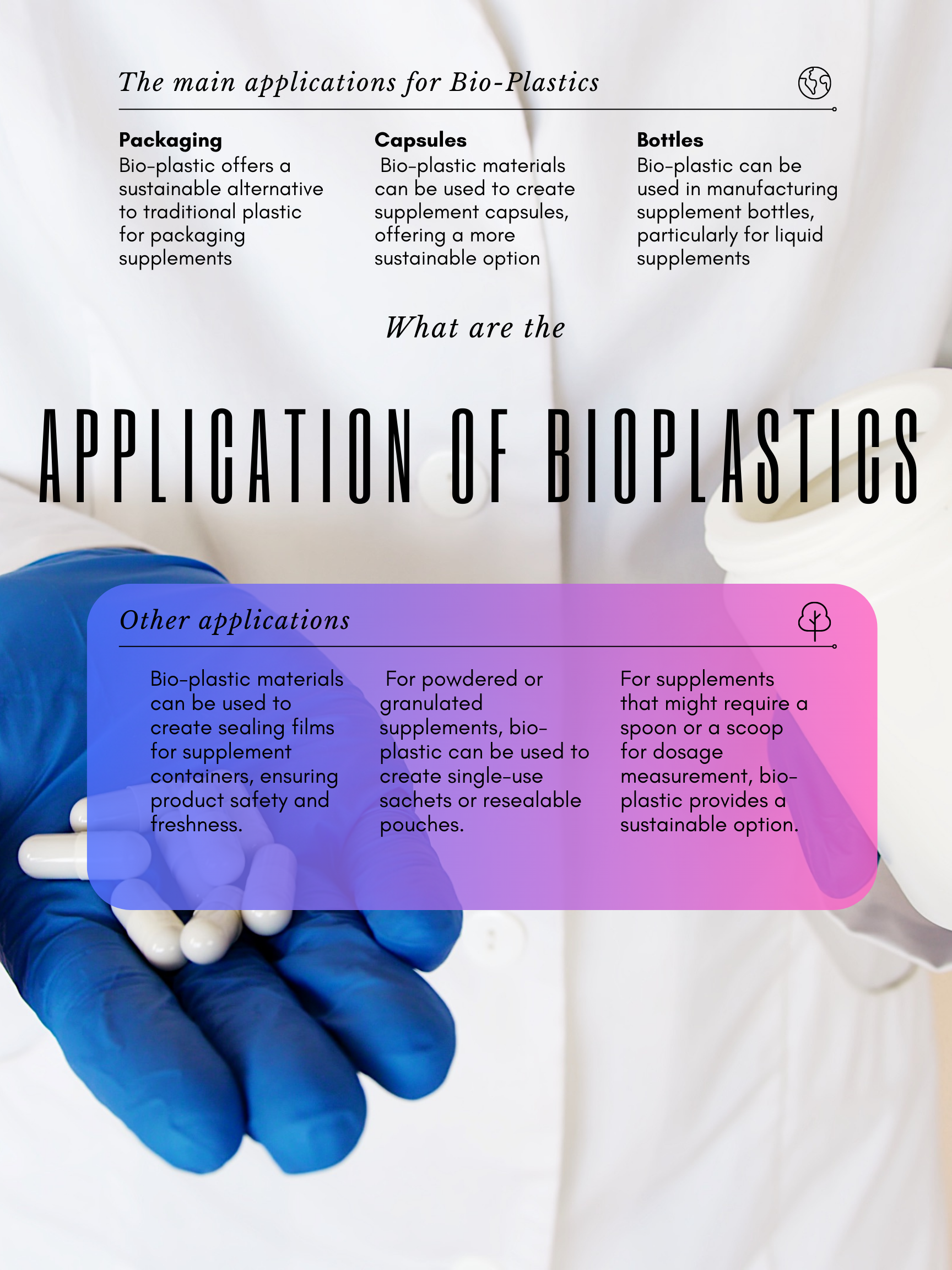
Enter Biobottles, an innovative company that has recognized the need for such radical transformation. Biobottles has developed a proprietary oxo-biodegradable plastic called PlasticIQ Technology, a sustainable solution for our plastic problem.
In stark contrast to traditional plastics, which fragment into the microplastics that wreak havoc in our environment, PlasticIQ Technology undergoes a process of oxo-biodegradation. This process ensures that plastic products made from this material degrade and then biodegrade completely over time into nothing more than carbon dioxide, water, and biomass. This transformation significantly reduces the risk of microplastic pollution, offering a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics.
By employing PlasticIQ Technology, Biobottles has successfully developed a new generation of eco-conscious plastic products. Their commitment to reducing plastic pollution is not just an ethical stand; it’s a revolutionary step towards sustainable business practices and the preservation of our planet.
Yet, the company’s efforts alone are not enough. This is a global problem that requires collective action. The reality of the situation is clear: unless we make conscious decisions to change our habits and preferences, the rise in microplastic pollution will continue unabated.
How can you, as individuals and businesses, contribute to this vital cause? The answer lies in the choices you make, every day. Choose products made from eco-friendly materials like those offered by Biobottles. Support companies that are committed to sustainable practices. Raise awareness within your community about the hazards of traditional plastics and the benefits of biodegradable alternatives.
If you are a business, consider transitioning to sustainable packaging solutions, like those provided by Biobottles. Not only will this demonstrate your commitment to environmental responsibility, but it will also resonate with a growing demographic of consumers who prioritize sustainability in their buying decisions.
In today’s world, where the harsh realities of environmental damage are more apparent than ever, it’s vital that we align our actions with the needs of the planet. Sustainable solutions like Biobottles’ PlasticIQ Technology give us the means to do so.
As we face the alarming rise in microplastic pollution, the call to action has never been clearer: It’s time to rethink our relationship with plastic. It’s time to embrace sustainable alternatives. It’s time to make the switch and become part of the solution. Together, we can safeguard our oceans, our planet, and our future.
Don’t wait for change; be the change. Make the conscious choice today. Choose Biobottles. Choose a cleaner, greener future for our world.