The Complexities of Plastic Recycling and Potential Solutions
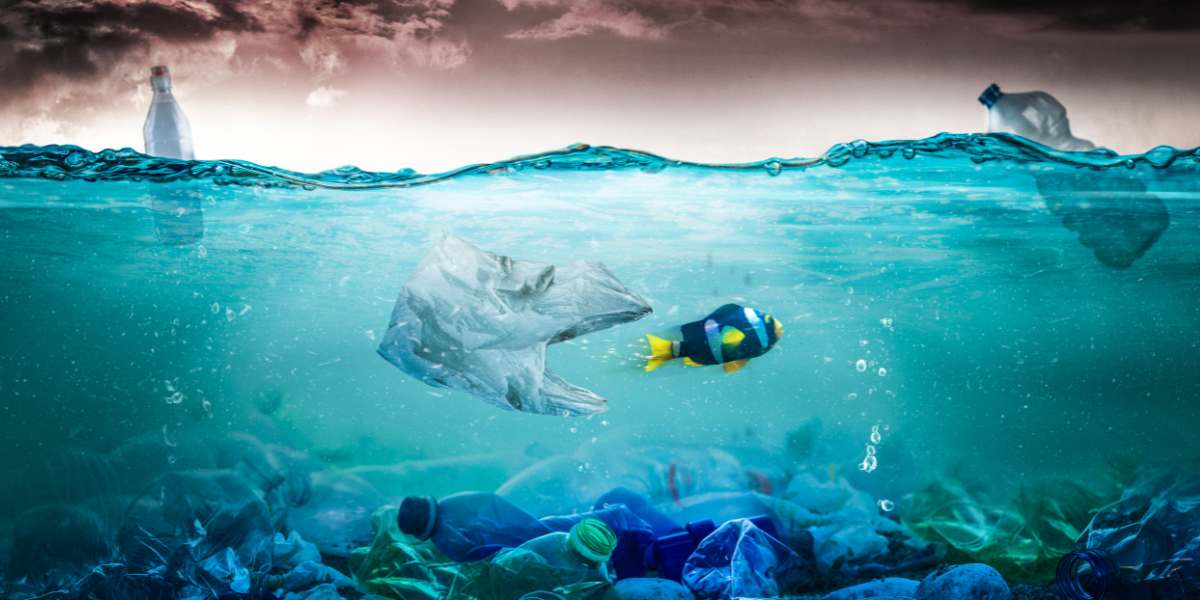
Recycling and composting have long been touted as the ultimate solution for plastic waste, a rapidly escalating global problem. The truth about plastic recycling, however, is complex and the process is not as straightforward as we once believed, as revealed in a recent in-depth video analysis. It discussed the challenges and complexities surrounding plastic recycling, with an emphasis on emerging solutions and a focus on Bio-Transformative Plastics as a viable alternative.
China Shuts its Doors to Plastic Waste
The video begins by examining the implications of China’s decision to stop accepting plastic waste from developed countries. The Chinese government cited the poor quality of incoming plastic as a significant issue, causing harm to their workers and environment. After accounting for healthcare and environmental remediation costs, they found it was no longer economically viable.
What Happens to Our Plastic Now?
With China out of the picture, other developing countries in Asia, like Malaysia, have become the go-to destinations for our waste. However, due to the lack of efficient waste management systems, much of this waste still ends up in landfills or incinerated, contributing to pollution.
Additionally, as we relied heavily on China for years, we’re now faced with a lack of developed domestic recycling infrastructure, leading to a closure of many collection and sorting operations. Municipalities like Philadelphia are turning to waste-to-energy plants, or incinerators, as an alternative, but this process may release harmful pollutants.
Changes in Recycling Regulations and the Role of Oceanworks
Regulators are reconsidering our recycling systems, with Maine leading the way as the first US state to adopt an Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) law for plastic packaging. This policy shifts the recycling costs from taxpayers to packaging brands and encourages the development of recyclable products and reuse schemes.
Oceanworks, an online marketplace, is attempting to create a market for recycled plastic independent of any specific country. They have established a supply chain for ocean-bound plastic, intercepting plastic before it enters the ocean and providing manufacturers with the raw material.
Oxo-Biodegradable Plastics: A Viable Solution
While the video explores numerous innovative solutions such as mushroom and algae-based packaging, it does not touch on the potential of Oxo-Biodegradable Plastics. An example of this is Biobottles, which decompose safely without leaving behind harmful microplastics, a significant environmental issue.
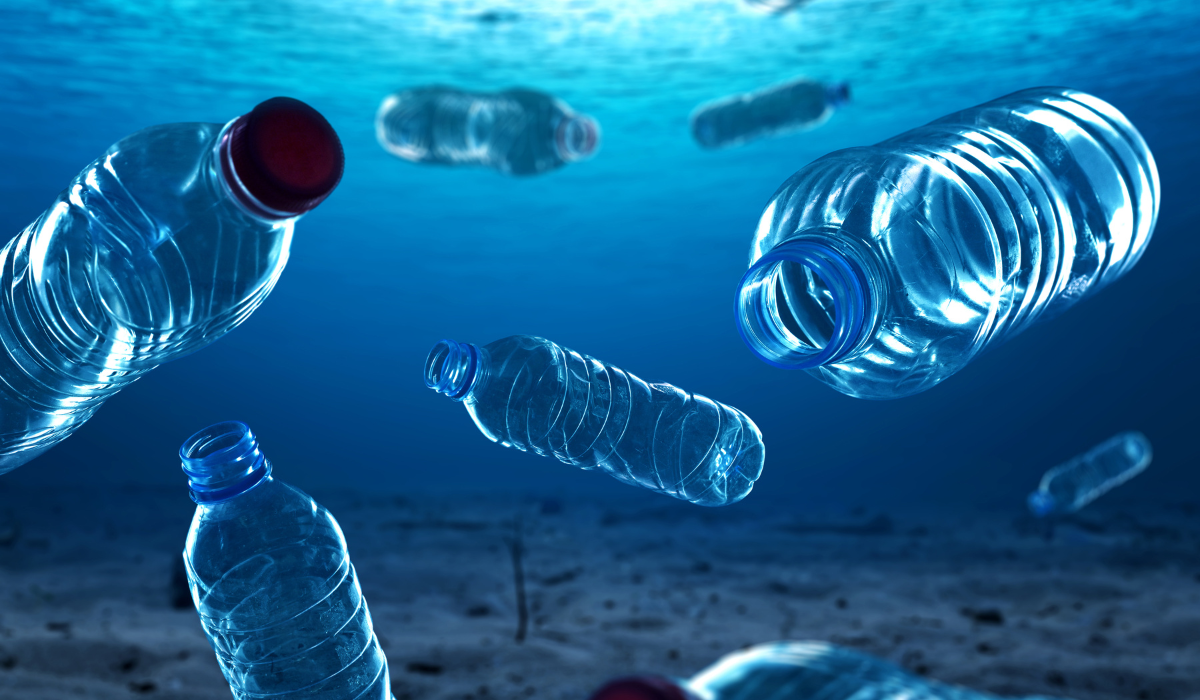
Oxo-biodegradable plastics are designed to degrade and then biodegrade in the open environment in the same way as nature’s waste. The process begins with the reaction of an additive with oxygen, leading to the breakdown of the plastic’s molecular structure over a pre-programmed period, leaving no harmful residues.
Biobottles made from Oxo-biodegradable plastics provide a significant solution as they disintegrate into biodegradable components without the release of microplastics, a leading cause of water and soil pollution.
The Future of Plastic Recycling
Clearly, plastic recycling is a complex system that needs continuous improvement to be a viable solution for our waste problem. As the video highlights, several initiatives are ongoing to improve the economic viability of recycled plastic. Upcycling methods and the use of alternative, plastic-free materials are promising future solutions.
However, in addition to these innovations, a shift in consumer behavior is crucial. We should strive to buy more plastic-free goods whenever possible and demand more transparency and accountability from the plastic industry and politicians. Oxo-Biodegradable Plastics like Biobottles, which leave behind no microplastics, are a viable option for a greener future.
This sustainable approach, combined with innovative recycling techniques and solutions, can help us overcome the growing global challenge of plastic waste. The road may be long, but the goal of a cleaner, healthier environment is within reach.
Bio-Transformative Plastics: A Deeper Dive
Bio-Transofrmative plastics, like Biobottles™, have emerged as an innovative solution to the problematic lifecycle of traditional plastic. Through an advanced process, these plastics break down into harmless, natural components without leaving behind harmful microplastics, which are a significant cause of pollution in water bodies and soil.
The technology behind these plastics involves the use of specific additives that cause the plastic to degrade when exposed to heat, light, and oxygen. This degradation process fragments the plastic into small, bio-assimilable materials that are consumed by microorganisms, completing the cycle back to nature. This approach contrasts sharply with conventional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to degrade, littering our landscapes and oceans with harmful microplastics.
Biobottles™, made from these Oxo-Biodegradable Plastics, are therefore designed with the environment in mind. By ensuring that they disintegrate into biodegradable components, the manufacturers take significant steps toward minimizing environmental damage caused by plastic waste.
The Importance of Conscious Consumer Behavior
While the production and recycling of plastic remain critical areas to address, consumer behavior plays a significant role in the bigger picture. By choosing to buy plastic-free goods or those made from Oxo-Biodegradable Plastics like Biobottles™, consumers can drive demand for more sustainable alternatives. Additionally, by demanding greater transparency and accountability from both the plastic industry and politicians, consumers can encourage a move towards improved waste management and recycling systems.
Looking Forward: A Multifaceted Approach
The future of plastic recycling undeniably involves a multifaceted approach. Recycling and upcycling initiatives must continue to evolve and adapt, providing economically viable and environmentally friendly solutions for plastic waste.
Innovations like Biobottles™ show great promise in their ability to reduce environmental damage. Still, they should be part of a broader effort to reduce the overall production of plastic waste, improving recycling infrastructure and encouraging the use of alternative, plastic-free materials.
Ultimately, the path to overcoming the global challenge of plastic waste will be paved with a mix of innovative solutions, conscientious consumption, and improved regulatory measures. With concerted effort and focus, a cleaner, healthier environment is an achievable goal.